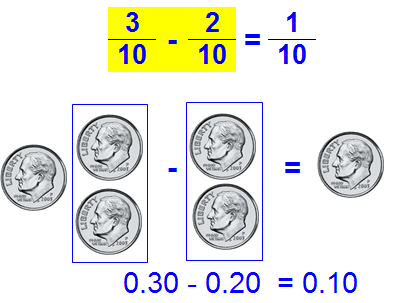
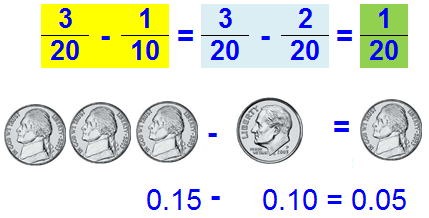
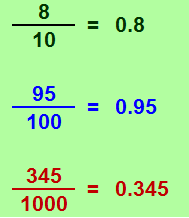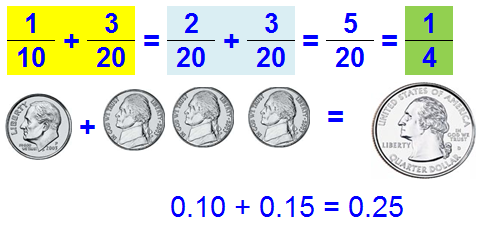A decimal is any number in our base-ten number system.
The position of the digit in the decimal number determines the digit’s value.
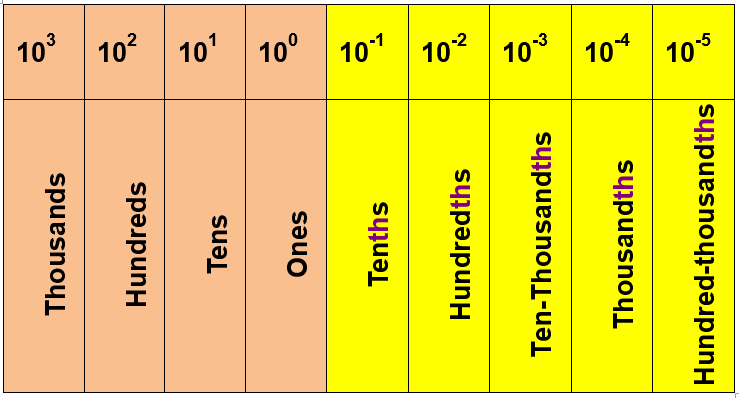
Decimals show numbers that are in between two whole numbers. A decimal has two parts, the integer part and the fractional part, which starts with the dot character. Example:
As an example of a decimal number, let’s take the number 65.894
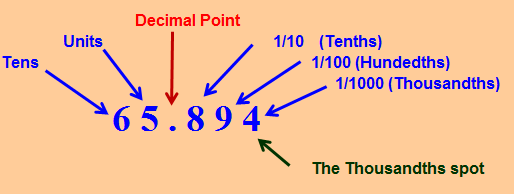
Sixty-five and eight hundred and ninety -four thousandths
The number after the decimal point can be collectively pronounced as 8 tenths, 9 hundredths and 4 thousandths or, more simply, as 894 thousandths.
Decimal Place Value Poem:
Reading Decimals is easy you’ll see,
They have two names like you and me.
First, you say the name as if there were no dot,
Then you say the name of the last place value spot!
Decimal values con be written as a decimal fraction (fractions with a denominator of 10, 100, 1000, …)
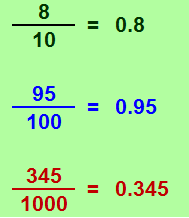
Decimal Standard Form to Word Names:
0.8 = eight tenths
0.95 = ninety five hundredths
0.345 = three hundred forty five thousandths
Hint: When writing a decimal number that is less than 1, a zero is normally used in the one´s place.
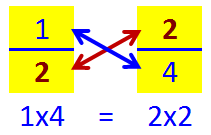
Comparing and Ordering decimals.
Comparing decimals is similar to comparing whole numbers. When we compare decimals we use place value.
1) Line Up Decimal Points
2) Start at the left and find the first place where the digits differ.
3) Compare the digits
Hint. Add zero’s to make all the decimals have the same place value name.
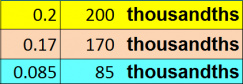
Example: Arrange the following numbers from least to greatest (in Ascending Order) 0.17, 0.085, 0.2
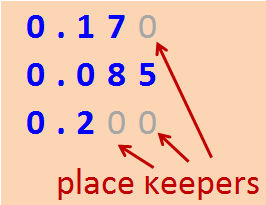
Align decimal points and place values, write a place keeper if needed. (Pretend it’s money)
Remember: Writing zeroes to the right of the decimal does not change its value
To arrange first make all decimal places same and comparing two decimals at a time.
0.085< 0.17
0.085 < 0.2
0.17 < 0.2
0.085 < 0.17 < 0.2
Ordering these decimals from least to greatest we get: 0.085, 0.17, 0.2
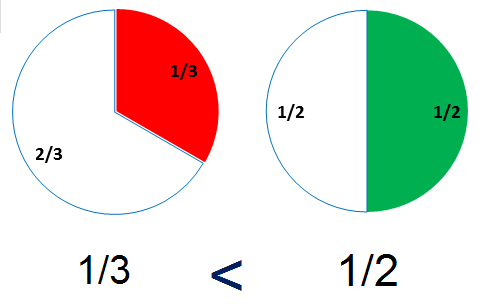
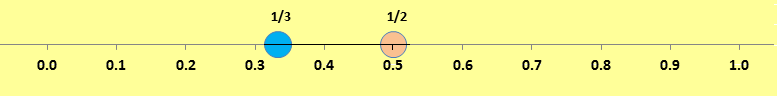
When we compare decimals we can use a number line.
Numbers to the right are greater than numbers to the left.
Example: Compare 3.6 and 3.25
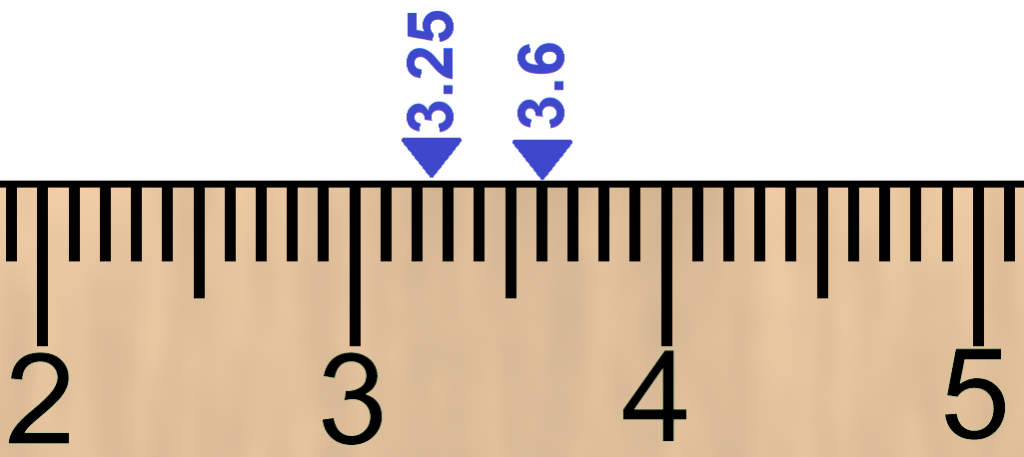
3.25 < 3.6

Three Steps to Round Decimals
(1) Underline the digit to be rounded
(2) Look at the number on the right of the underlined number.
* If it’s 5 or more, add one more to the underlined number.
* If it’s 4 or less, keep the underlined number the same.
(3) Eliminate the digits beyond the place being rounded.
Example:


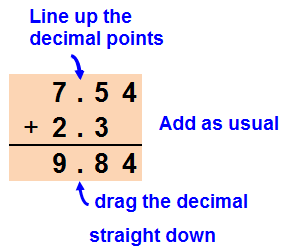
Add/Subtract decimals.
(1) Align your decimal point and place value.
(2) Write place keepers if needed
(3) Add or subtract
(4) Keep your decimal point.

Add Decimals
Adding, Subtracting Decimals Help

Subtract Decimals A
Subtract Decimals B

To multiply a decimal number by a whole number
Ignore the decimal point and multiply the digits. Place the decimal point in the answer so that it has the same number of decimal places as the number being multiplied
Ex: 2.22 X 43 = 95.46


Multiply Decimals by powers of ten
0.5 x 10 = 5
0.5 x 100 = 50
0.5 x 1000 = 500
0.5 x 10000 = 5000
Hint: Just move the decimal point one place to the right for each zero you see after the 1
To multiply a decimal by a power of ten, just move the decimal point to the right as many times as there are 0’s. (Add 0’s if there are not enough digits).

Divide decimals by powers of ten

0.5 ÷ 10 = 0.05
0.5 ÷ 100 = 0.005
0.5 ÷ 1000 = 0.0005
0.5 ÷ 10000 = 0.00005
You can divide by powers of 10 simply by moving the decimal point one space to the left for every zero in the power of 10 that you are dividing by. (Add 0’s if there are not enough digits).

To multiply a decimal number by a decimal number
Ignore the decimal points and multiply the digits; count the total number of decimal places in both decimal numbers being multiplied; and place a decimal point in the answer so that it has the same number of decimal places as the total number of decimal places in the two numbers being multiplied

To divide a decimal number by a whole number
In order to divide the given decimal number by the given whole number use Long Division (ignore the decimal value). Now place the decimal value at the place the dividend has before.

To divide a decimal number by a decimal number
Move the decimal point in the divisor to the right until it is a whole number.
Move the decimal point in the dividend to the right by the same number of places as the decimal point was moved to make the divisor a whole number.
Then divide the new dividend by the new divisor

Divide Decimals by Decimals