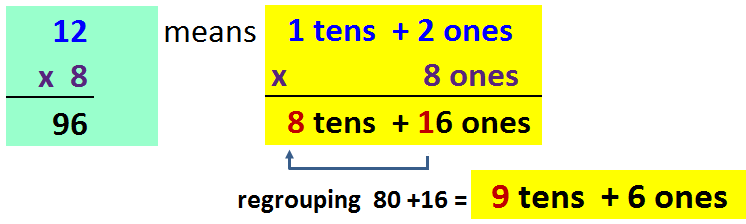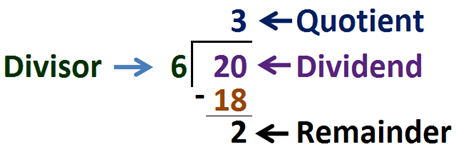Multiplying whole numbers
Multiplication is a mathematical operation that indicates how many times a number is added to itself.
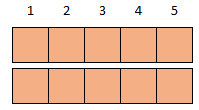
2 x 5 = 10 5 + 5 = 10
Multiplying two groups of 5 Adding two groups of 5
Multiplication is repeated addition. Add repeatedly (or skip-count) to multiply
2 x 5 = 10
2 x 5 = 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 10
Multiplicand is a number that is to be multiplied by another (the multiplier). Product is the result of multiplying two (or more) numbers, for instance, 10 is the product of 2 and 5.
Factors are the numbers that are multiplied together.
Long multiplication (traditional method)
In this method we multiply the multiplicand by each digit of the multiplier and then add up all the properly shifted results.
Steps:
Step one: Multiply by ones digit to get the first partial product.
Step two: Multiply by tens digit to get the second partial product.
Step three: Multiply by hundreds digit to get the third partial product.
Step four: …
Last step: Add all partial products together to get the final product!
Example:
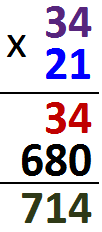
In this example, we multiply by the units and the tens separately.
34 x 21 = 34 x (20 + 1) = 34 x 20 + 34 x1 =680 + 34 = 714
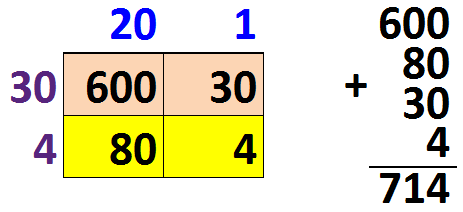
The box method (partial products method) works by splitting each number into tens and units
Example: 34 = 30+4 and 21 = 20+1
34 x 21 = 600+80+30+4 = 714
Multiply_Integers
On a separate sheet of paper, multiply and check your answers.
Dividing whole numbers
Division evaluates how many times one number is present in another number.
Division is splitting into equal parts.
Example: 10 ÷ 2 = 5
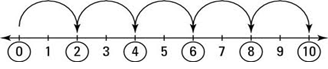
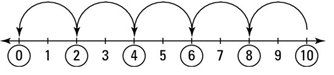
Division is repeated subtraction.
(1) 10-2 = 8
(2) 8-2 = 6
(3) 6- 2 = 4
(4) 4-2 = 2
(5) 2-2 = 0
5 is the number of times you can subtract 2 from 10 before you get to 0.
The number that gets divided is called the dividend.
The number that does the dividing is called the divisor.
The answer obtained after division is called the quotient.
Dividing two integers may result in a remainder. The remainder is the number left over when a number cannot be divided evenly by another number.
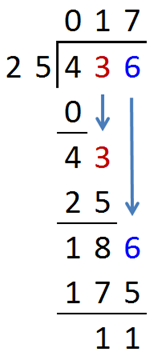
Long division algorithm:
1) Divide;
2) Multiply;
3) Subtract;
4) Bring down the next digit.
Example:
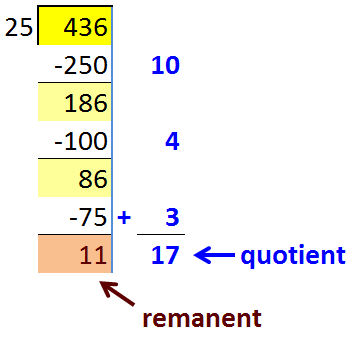
The ‘chunking’ method (or partial quotients method) uses repeated subtraction to find answers to division problems.
In this method, we repeatedly take away “chunks” of the large number that are subtracted from the total.
Dividing Whole Numbers with Remainders
Multiply and Divide Whole Numbers
Solving Equations By Multiplying or Dividing
Word Problems – Using Whole Numbers
Any division of whole numbers can be written as a fraction.
1-Digit Divisor; 2-Digit Quotient
1-Digit Divisor; 3-Digit Quotient
1-Digit Divisor; 4-Digit Quotient
1-Digit Divisor; 5-Digit Quotient
2-Digit Divisor; 2-Digit Quotient
2-Digit Divisor; 3-Digit Quotient
2-Digit Divisor; 4-Digit Quotient
3-Digit Divisor; 3-Digit Quotient
3-Digit Divisor; 4-Digit Quotient